"Ideal" format:- film format in the proportion of 4 to 3, e.g. 6 x 4.5cm. This ratio is considered the ideal shape by some manufacturers and many photographers for both vertical and horizontal composition.
IF (Internal Focusing):-system in which only the internal lens group shifts during focusing. IF benefits include focusing without changing the physical length of a lens body, faster focusing, reduced diameter of the focusing ring, closer minimum focusing distance, and aberrations corrected throughout the entire focusing distance range.
Illuminance:- term quantifying the illumination of, or incident light falling on a surface.
Image:- two dimensional representation of a real object, produced by focusing rays of light.
Image plane:-plane commonly at right angles to the optical axis at which a sharp image of the subject is formed. The nearer the subject is to the camera, the greater the lens image plane distance.
Impressionism:- art movement in which painters broke away from the techniques of continuous brushstrokes and clearly expressed detail. They were largely concerned with the effects of light and color.
Incident light:- light falling on a surface, as opposed to reflected by it.
Incident light attachment:- accessory for a hand held exposure meter which allows it to give incident light readings. Many models come with this accessory permanently attached.
Incident light reading:- measurement, by light meter, of the amount of incident light falling upon a subject. The light meter is placed close to the subject, pointing towards the main light source.
Indicator chemical:- neutral chemical which can be added to a sample of a solution to indicate its pH level or the presence of hypo.
Infectious development:- development action which occurs in processing "lith" materials. The oxidation of hydroquinone produces new and highly active reducing agents, semiquinones, in the presence of a low quantity of sodium sulfite. This results in a very high contrast image.
Infinity:- in photographic terms is a distance great enough to be unaffected by finite variations. In practice this relates to most subjects beyond 1000 meters or, in landscape terms, the horizon.
Infrared:- rays that occur beyond the red end of the electro-magnetic spectrum and are invisible to the human eye. They can be recorded on specially sensitized films, producing images in black & white or color.
Infrared compensation index:- used to compensate the focus for black and white infrared film. Color IR film generally does not require compensation.
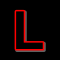
Infrared focus:- see IR setting.
Instamatic camera:- compact camera popular in the 1960s and 70s with very simple controls, taking 126 film and yielding a 28 x28 mm negative.
Instant picture camera:- camera, usually with simple controls, producing a finished photographic print within minutes of the film being exposed, (e.g. Polaroid cameras and materials).
Integral tri-pack:- three emulsions, usually of different character, coated on the same film base. The system is used mainly on color materials and also on some special purpose black & white materials.
Integrating:- term used to describe a method of arriving at an exposure setting by taking an average of the light readings from the bright areas and the and the shadow areas of the subject.
Intensification:- chemical method of increasing the density of the photographic image. It is only suitable for treating negative materials and works better on negatives that have been underdeveloped rather than underexposed.
Intensity scale:- exposure scale in which the time of exposure remains constant but the intensity of light increases in regular stops.
Interchangeable lens system:- system of lenses of different focal lengths made to fit the same camera body.
Interference:- interaction of light waves when they meet and either reinforce or cancel each other (e.g. holograms).
Interleaving:- method of agitating more than one sheet of photographic paper in the same tray of chemicals.
Intermittency effect:- states that, a number of short, separate exposures will not produce the same photographic result when combined as a single exposure of equivalent total duration.
Internegative:- negative made on special color film designed for making copy prints from color slides.
Intersection of thirds:- compositional technique whereby the image area is divided horizontally and vertically into equal thirds by means of four imaginary lines. The main subject is considered strongly placed it it is positioned at the intersection of any two of these lines.
Interspersed aspect ratio:- basic requirement of certified photofinishers and certified photo finishing equipment. It specifies the three APS system print formats - C, H and P.
Inverse square law:- states that, when the light source is a point, illumination on a surface is inversely proportional to the square of the distance of the light source.
Inverted telephoto lens:-lens construction which gives a short focal length with a long back focus or lens-film distance. It enable wide-angle lenses to be produced for small format cameras, where space is required for mirrors, shutters, etc.
Iodine:- chemical used in reducers and bleachers.
Iris diaphragm:- continuously adjustable lens aperture consisting of interposed metal leaves.
Irradiation:- by the physical structure of the emulsion and the distribution of the silver halide grains cause rays of light to be scattered as they travel through the emulsion.
IR setting:-mark usually in red, found on many camera lens mounts. It indicates the focus change required for infrared photography.
IS (Image Stabilizer):- feature that minimizes the effects of camera shake. Originally designed for video cameras. Canon has transferee the technology to its EF lenses.
I setting:- mark found on some cheap box cameras which indicates an instantaneous shutter speed of approximately 1/50 second.
ISO:- International Standards Organization. Used instead of ASA as prefix to film speeds. The scale is identical to the ASA scale.
Ivorytype:- obsolete printing process designed to give the impression of a painting on ivory. A hand colored print was impregnated with wax and squeegeed face down on hot glass. The paper base was then back by ivory tinted paper.
IX (Information Exchange):- ability of APS film to communicate with devices, and devices to communicate with film.